Authors:
Ghazal Bangash, Pierre-Adrien Forestier, Loutfouz Zaman
Until recently, video games could be played only on gamers' personal computers or gaming consoles, which has been the norm for decades. But the restrictions of this local hardware have been a regular source of frustration for both developers and players. On the player side, getting your hands on the latest gaming experiences can be very costly, involving high-priced gaming rigs and console updates. With each new technological development comes an increase in the necessary hardware, and some gamers are unable to keep up. And so the cycle continues. On the development side, in addition to creative skill, high-powered testing and rendering gear are essential for making visually stunning video games. This causes a strain on development resources; in turn, creativity is hindered as the processing power needs rise in tandem with the complexity and realism of gaming worlds.
→ Cloud gaming services revolutionize gaming by making high-quality games accessible without expensive hardware.
→ Developers enjoy streamlined collaboration and efficient creation, while players experience enhanced realism and cross-platform play.
→ Despite these benefits, challenges such as reliable Internet access and environmental sustainability must be addressed.
With the rise of game streaming services, the video game industry has seen a dramatic transformation. There will still be a strong demand, however, for locally played games and tangible media to satisfy the preferences of collectors, traders, sharers, and physical media enthusiasts. Similar to how services like Netflix have transformed the way people watch movies and TV shows, these services are changing the way people play video games. Digital and streaming alternatives are becoming more popular in the entertainment industry, and this shift reflects that. These options provide more variety and ease of use, but they still require Internet access and subscription models. Services like Amazon Luna, Xbox Cloud Gaming, PlayStation Now, and Nvidia's GeForce Now are some well-known examples.
The core technology behind cloud gaming is the use of powerful servers located in data centers to handle processing and rendering tasks. When a player starts a game session, a distant server takes in their orders, processes them, and then renders the game frames. The player's device then receives real-time audio and visual stimulation. The player's device acts as a client, receiving the game stream and communicating with the server to deliver input requests. Mobile phones and set-top boxes do not always have the specs to run high-quality video games, but cloud-based gaming services are working toward that goal.
Not only does cloud gaming change the game for players, but it also has far-reaching consequences for the industry as a whole and the future of video game development. Here, we will take a look at how the future of gaming is being shaped by technological developments that have made gaming richer, how games are becoming more accessible to more people, how cloud gaming is helping players be more creative and collaborative, and how all of these things are coming together.
Figure 1 depicts the architecture of cloud gaming, which also shows how network infrastructure, data centers, and player devices interact. All tasks related to processing and rendering games are handled by strong servers outfitted with cutting-edge CPUs and GPUs within the data center. The player's device, which may be a PC, console, smartphone, or tablet, receives the processed game stream via specialized streaming protocols via a high-speed Internet connection. The player's device, which receives the game stream, records user inputs, and displays the game with matching audio, ensures a smooth and engaging gaming experience. Because of this architecture, gamers can enjoy high-quality games across a range of devices without requiring expensive local hardware.
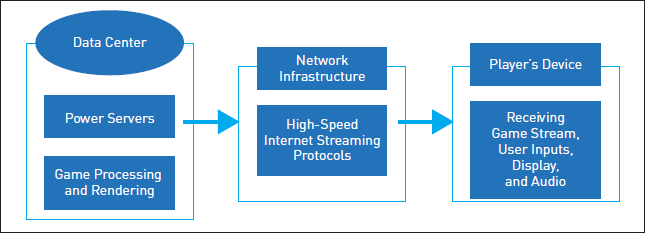 | Figure 1. The architecture of cloud gaming, highlighting the interaction between data centers, network infrastructure, and player devices. |
 Expanding the Single-Player Experience
Expanding the Single-Player Experience
Already, cloud computing has revolutionized multiplayer gaming by facilitating instantaneous, fluid interactions in massive, densely inhabited virtual worlds. Massive multiplayer online games hosted in the cloud allow players to enter enormous virtual worlds populated by thousands of other users who can interact with one another in real time. This helps players stay in sync and minimizes latency, which in turn attracts more serious gamers from all over the world.
Two possible outcomes of integrating cloud technologies into single-player gaming are an increase in the amount of content a player may consume and individualized experiences through behavior-based customization. This idea isn't new to cloud gaming; it has been implemented in games made for local hardware before, for example, as games with branching plots. The 2015 game Until Dawn from Supermassive Games is a prime example. Game storage requirements are directly proportional to the number of stories and personalization options. This holds true even for games that primarily follow a linear plot yet have a wealth of substance and story, as video games have been continuing to grow in size [1]. Although precise data on the average size of a typical PS5 game is not readily available, due to the continuously increasing library of games, anecdotal observations suggest the increase has been observed not only from the PS4 and PS5 versions of the same games, but also between the popular games at the launch of PS5 and today. For example, compared with Final Fantasy VII Remake (Square Enix, 2021), which was released closer to the launch date of PS5 and takes up 86 GB of space, Final Fantasy VII Rebirth (Square Enix, 2024), which was recently released on two PS5 discs, takes up a whopping 145.7 GB [2]. Electronic Arts' Star Wars Jedi: Survivor (2023) is another example in the same genre, clocking in at 148 GB. As of May 2024, the most massive game on PS5 is Call of Duty: Black Ops Cold War (Treyarch/Raven Software, 2020), clocking in at 312.6 GB. On an early PlayStation 5 model with 667 GB of available space, installing one of these games would probably necessitate removing other titles to create room.
It would be possible to revolutionize the gaming experience if developers were not limited by the capabilities of players' solid-state drives (SSDs) and game content were instead saved and streamed from the cloud. Instead of recycling game assets and locations, developers might inject more original content into games with linear plots. Take Elden Ring (FromSoftware, 2022) as an example. The dungeons feature 104 boss encounters, of which only 32 are unique [3]. Furthermore, there is potential for games with individualized storylines and adaptive landscapes to have a longer shelf life than what is now possible with SSD restrictions. This is because these games offer more depth and longer replay opportunities.
Cloud computing provides many advantages for developers who want to build games that re-create intricate ecosystems or provide expansive settings. For example, to create an incredibly lifelike flying experience that couldn't be achieved by storing the data locally on a console or PC, games like Microsoft Flight Simulator leverage the cloud to broadcast high-fidelity, real-world geography and weather data in real time. Specifically, Microsoft Flight Simulator takes advantage of the Azure cloud platform. The game's realistic atmospheric modeling and real-time weather conditions are made possible by using over 2.5 petabytes of Bing Maps data. This data contains more than 37,000 airports, 2 million cities, 1.5 billion buildings, 2 trillion trees, and 117 million lakes [4].
Cloud computing provides advantages for developers who want to build games that re-create intricate ecosystems.
 Enabling More People to Enjoy High-Quality Video Games
Enabling More People to Enjoy High-Quality Video Games
Cloud-based rendering has also brought forth a new era of player accessibility. In the past, many would-be gamers have been put off by the traditional high-end hardware requirements. Cloud gaming has therefore had a revolutionary impact in areas where high-performance gaming gear is either not available or too expensive. As a result, players in these regions can now join the worldwide gaming community and enjoy top-tier experiences on par with gamers using powerful PCs, immersing themselves in aesthetically breathtaking realms that were previously unreachable. Thanks to the cloud, any device—a cheap laptop, tablet, or smartphone—can access high-quality gaming.
The ability to deliver smooth rendering on cloud servers also paves the way for cross-platform gaming. Players may pick up where they left off when they move between devices, and there will be no noticeable drop in performance or visual quality. The flexibility of the gaming environment is a boon, as it fosters more-interconnected groups and helps spread gaming culture further afield.
A number of games and platforms have documented this in the past few years. The now-discontinued Google Stadia made high-end video games accessible to more people, allowing casual gamers who are not willing to invest a lot of money enjoy titles like Assassin's Creed Odyssey (Ubisoft, 2018) and Cyberpunk 2077 (CD Projekt Red, 2020). Cyberpunk 2077 had performance issues on both PCs and consoles when it was released [5]. Google Stadia users, on the other hand, said that even without top-tier gear, Cyberpunk 2077 ran well [6].
Playable on player-owned devices including smartphones and tablets, Xbox Game Studios' Halo Infinite (2021) and Forza Horizon 5 (2021) were released by Xbox Cloud Gaming. Bloodborne (FromSoftware, 2015) and Uncharted 4: A Thief's End (Naughty Dog, 2016) were both made available on multiple devices on PlayStation Now. Also seen on Nintendo Switch are cloud versions of Hitman 3 (IO Interactive, 2021) and Control (505 Games, 2019), which allow for high-graphical-fidelity rendering of expansive environments and intricate levels on a low-powered handheld console from the previous generation.
Among the most compelling aspects of cloud gaming are its quick playability and cross-platform continuity, which reflect the changing interests and lives of players. These days, a lot of people would rather not deal with installing or updating their games or with costly gaming hardware and just want to play their games right now. This reflects current trends in online video and music streaming. The majority of consumers are willing to sacrifice small differences in quality that they might barely notice for the convenience of streaming services. However, there is still a market for high-end enthusiasts who enjoy movies on Blu-ray discs at the highest bit rates, in their home theaters, on large, high-quality OLED displays with high dynamic range (HDR) perfect blacks, and with 7.1.4 Dolby Atmos surround sound.
 Collaborative Gameplay and User-Generated Content
Collaborative Gameplay and User-Generated Content
With its focus on user-generated content and cooperative gameplay, cloud gaming platforms are causing a sea change in the gaming industry. Thanks to the tools made available by the cloud, players can now transform into producers, sharing their own unique game material with the world. Sandbox games are a prime example of this change, as they allow players to build elaborate structures, vehicles, and even entirely new game concepts. By making these things and sharing them with other gamers, developers can keep the game alive for longer and encourage a creative ecosystem to flourish. Two well-known examples of this type of game are Roblox (Roblox Corporation, 2006) and Minecraft (Mojang Studios, 2011).
Thanks to advancements in cloud computing, gamers from all over the world may now work together in real time to create and shape virtual environments. For example, in a sandbox game played via the cloud, people might collaborate on building complex cities, riddles, and narratives. This collaborative approach enhances the gaming experience and fosters a sense of community and shared achievement.
The modding scene has also been transformed by cloud platforms. The usage of cloud-based technologies has made it easier for modders to make and share their mods, which increases the mods' reach and accessibility. As a result, there is now an abundance of user-generated material, with modifications varying from subtle style tweaks to radical changes to game mechanics.
 Cloud Gaming from the Developers' Perspective
Cloud Gaming from the Developers' Perspective
These increasingly popular cloud infrastructures offer an extensive range of communication, storage, and computing resources in an economical, dependable, elastic, high-performance, low-maintenance way, not only for players but also for developers. Cloud gaming both allows developers to create games more easily with lightweight hardware and helps them build games that could reach a large audience pool. Cloud gaming reduces the entry barrier for players by reducing the need for users to buy pricey gaming hardware. As a result, more people trying out new games may boost sales and generate more revenue for the developers.
One important issue that developers often face is being able to synchronize on the code level with their team members. Three-dimensional development requires powerful, specialized hardware for each team member in traditional setups. Working together requires synchronizing resources across several computers, which frequently causes delays and inefficiencies. The procedure is economically taxing and incredibly slow. Cloud gaming platforms, on the other hand, may provide Web access for anyone creating or using a 3D application worldwide. No more compatibility issues or device constraints—simply access the application through your browser and immerse yourself in the experience.
Another issue is ineffective delivery of applications. Applications developed with conventional 3D engines are complicated to deliver. Every target device requires a different build and packaging procedure, and hardware capabilities still determine the final user experience. On the other hand, switching to Web-based delivery provides a more seamless experience. Its improved security options and inherent optimization make it more efficient to deploy and guarantee a more consistent player experience across different devices.
Figure 2 outlines the benefits of integrating cloud gaming technology into the game development process. The process starts as soon as game development is started, at which point the team plans, designs, and codes the game. Then, developers use cloud-based collaboration tools, such as real-time editing platforms and shared repositories, to allow team members to collaborate concurrently from different locations and guarantee access to the most recent project versions. Subsequently, the development process makes use of cloud infrastructure to lower hardware costs and enable scalable computing resources for tasks like creating, testing, and deploying game components. Cloud platforms are utilized for the final game's deployment, enabling widespread distribution and user-friendly accessibility. This method makes high-quality games available on a variety of platforms, including smartphones, tablets, and PCs, and guarantees timely updates. The figure illustrates how cloud gaming technology facilitates more user access to high-quality games without requiring expensive hardware by improving collaboration, lowering hardware requirements, and enabling efficient application delivery.
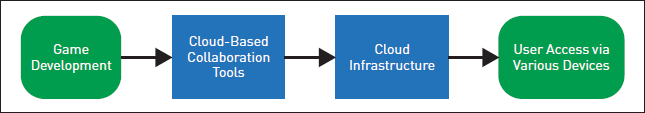 | Figure 2. Workflow diagram outlining the benefits of integrating cloud gaming technology into the game development process. |
It is clear that cloud-optimized rendering technologies are leading a revolutionary shift as we imagine the gaming scene of the future. The game creation process is likewise undergoing a transformation due to these advances, which are democratizing access to high-quality gaming experiences for users worldwide. The indie scene in particular benefits from cloud gaming because it gives creators the tools they need to collaborate and be creative more efficiently, which in turn creates an atmosphere that is diverse and innovative. This mutually beneficial connection between technical progress and artistic liberty is expanding the boundaries of what is possible in video games, making for an interactive, user-friendly, and ever-changing virtual environment. There are still, however, unsolved problems when it comes to cloud gaming. Reliable, constant, and fast Internet connections may not be readily available ubiquitously, which can be an obstacle to wider adoption. Perhaps more important concerns are those around environmental sustainability, as research has shown that a 112 percent increase in gaming-related carbon emissions would occur if cloud gaming followed a "streaming as norm" scenario, which would include 90 percent of players migrating to the cloud and rendering games at modest resolutions [7].
To sum up, cloud gaming presents a significant step forward, which promises a more inclusive, innovative, and immersive future for gamers. It also presents new challenges and opportunities that the industry must address.
1. File sizes of triple-a game. Kingston Technology Company. Aug. 2023; https://www.kingston.com/en/blog/gaming/file-sizes-triple-a-games-2023
2. Jackson, C. Here's how much space you need to clear for Final Fantasy VII Rebirth. Kotaku. Feb. 27, 2024; https://kotaku.com/final-fantasy-7-rebirth-install-size-download-preload-1851289668
3. Varnson, F. How many bosses Elden Ring actually has. Screen Rant. May 28, 2022; https://screenrant.com/elden-ring-bosses-how-many-battles-fights/
4. Microsoft Flight Simulator: The future of game development. Microsoft Game Dev Blog. Jul. 15, 2021; https://bit.ly/45jyK5L
5. Porter, J. Cyberpunk 2077 developer says disappointed players can ask for refunds. The Verge. Dec. 14, 2020; https://www.theverge.com/2020/12/14/22173738/cyberpunk-2077-developer-apologizes-base-ps4-xbox-one-performance-issues-refunds
6. Zwiezen, Z. Cyberpunk 2077 is surprisingly fine on Stadia. Kotaku. Dec. 10, 2020; https://kotaku.com/cyberpunk-2077-is-surprisingly-fine-on-stadia-1845853147
7. Marsden, M., Hazas, M., and Broadbent, M. From one edge to the other: Exploring gaming's rising presence on the network. Proc. of the 7th International Conference on ICT for Sustainability. ACM, New York, 2020, 247–254.
Ghazal Bangash is a master's student at Ontario Tech University working on extended reality (XR) technologies. [email protected]
Pierre-Adrien Forestier, cofounder and CEO of 3dverse, draws upon 15-plus years of experience at Microsoft, where his expertise revolved around crafting industry solutions with core Microsoft technologies. As CEO of 3dverse, he spearheads innovation within the cloud-based real-time 3D platform with the ultimate vision of empowering developers to build 3D business applications that address industry challenges. [email protected]
Loutfouz Zaman is an associate professor at Ontario Tech University, where his research focuses on advancing game development and evaluation. His areas of interest include visual game analytics, user experiences in gaming, utilizing deep learning for detecting bugs in games, emotion analysis of players using computer vision, and serious and exergames. [email protected]
Copyright held by authors. Publication rights licensed to ACM.
The Digital Library is published by the Association for Computing Machinery. Copyright © 2024 ACM, Inc.






Post Comment
No Comments Found